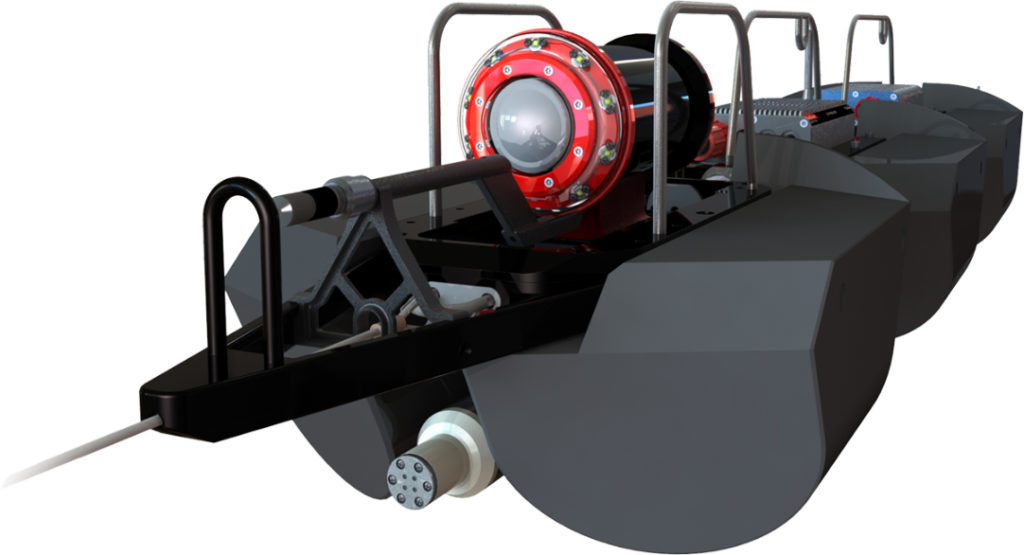
While routine CCTV investigation is a beneficial tool for subjective analysis, it can be difficult to quantify and measure remaining useful life from a video image. Failure is not an option for large diameter pipes, so any inspection data must be useful. Laser sensors provide the foundation for a proper, preventative condition assessment.
What’s the Difference? 2D vs. 3D Laser Inspection
Incorporating laser-based inspection complements and enhances what is visually seen with CCTV. This can also better detect and measure the changes in pipe shape caused by corrosion, deterioration, deformation, and deflection. Laser-based inspection comes in two types: laser profiling or ring laser (2D) and LiDAR (3D). Laser profiling is more commonly utilized for pipeline inspection in comparison to its 3D counterpart. This is because it offers a simpler deployment method and interpretation of the inspection results. Many Snap-On laser profilers are available for mounting to conventional CCTV equipment.
How does 2D laser profiling work?
Laser profiling projects a beam of light onto a surface and records it with a camera. This circular beam, or ring, is extensively calibrated with the conical lens of that camera. This allows for accurate collection of data as the circle passes over variations in the pipe surface as the robotic platform moves down the pipe.
The collected scans are then turned into cross-sections. These cross-sections are compared to the expected internal diameter of the pipe using profiling software. Measurements that are inside the reference shape indicate a presence of buildup or debris. Measurements that are outside the reference shape indicate corrosion, deterioration, or deformation; depending on the pipe material. 2D scans can also be used for confirming shape and size changes in the pipe geometry.
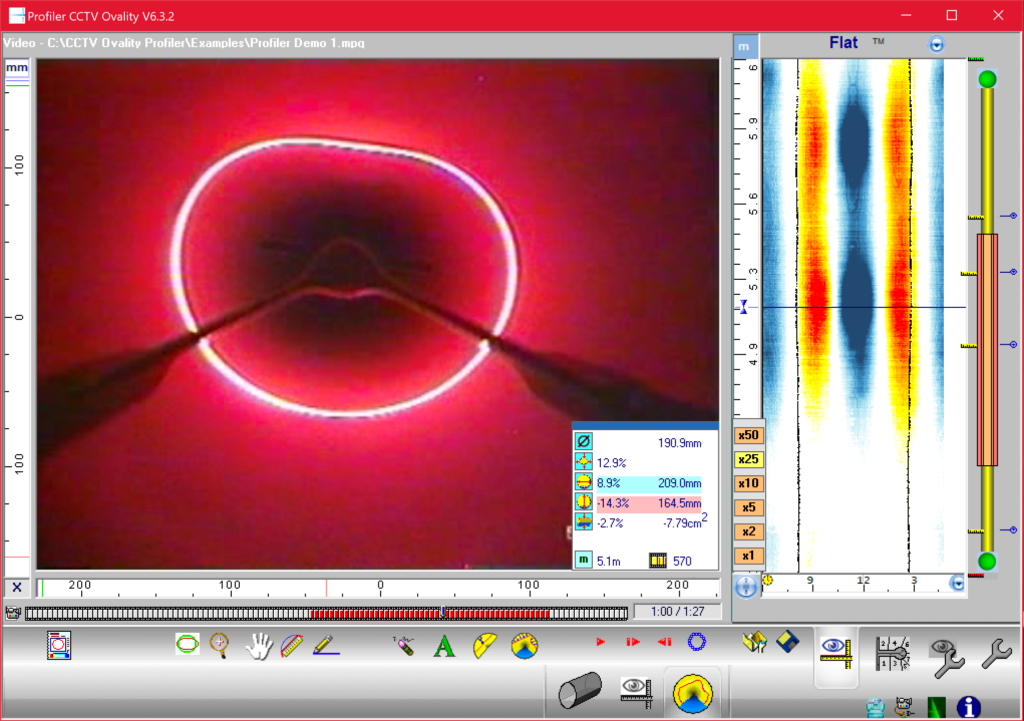
It is important to note that profiling laser does have limitations. Laser can only be used on un-submerged sections of pipe, and it cannot measure through bends of a pipe. The circular nature of the beam of light has a tendency to appear as an oval in the bend as the robotic transport cannot keep a consistent directional heading, often bumping into the outer walls. Once it has passed through the bend, however, accurate analysis can continue.
Laser profiling helps system owners answer the most important questions
The results from a profiling laser inspection are used to answer a number of key questions for underground asset management.
- What is the true structural condition of my large diameter line?
- Which trunk or interceptor do I need to rehabilitate first?
- For this lined pipe, how do I check for ovality or deformation or contractor compliance?
- What is the remaining useful life (RUL) of this asset?
By quantifying the deterioration and degradation of a line using a laser, a utility owner can eliminate the guesswork when it comes to rehabilitation and planning. This allows for proper prioritization and actionable preventative maintenance to extend the life of the asset. Additionally, multiple laser inspections spread out over several years provides a glimpse into how the pipe changes by measuring the rate of change; informing your preventative maintenance plan for years to come.
2D laser profiling is available on our Profiler platforms: MD Profiler and SuperMD Profiler.